From birth until the first year of life, an infant’s immune system develops dramatically. This period is critical because the newborn transfers from the sterile environment of the womb to the world outside, which is teeming with new germs. Understanding how the immune system develops during this period can benefit both parents and healthcare providers.
The Initial Contact with the World
A baby’s immune system is somewhat immature at birth, but it does have several crucial skills inherited from its mother. These include passive immunity, which is transmitted by antibodies found in the placenta during pregnancy and breast milk after birth. These antibodies form the infant’s initial line of protection against infections.
The Role of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is critical for the development of the baby immune system. Breast milk contains antibodies, immune cells, and other chemicals that help infants fight infections in addition to providing critical nutrients. Furthermore, it promotes the growth of a healthy gut microbiota, which is necessary for the development of a strong immune system. According to studies, the gut microbiota regulates immune system maturation and aids in the establishment of antigen-specific oral tolerance.
Immune System Maturation
The first year of life marks a period of fast immune system growth. Initially, children rely heavily on innate immunity—the body’s initial response to infections. As they mature, they gain adaptive immunity through exposure to microorganisms and vaccinations. This component of the immune system employs specialized antibodies and immune cells to recall and respond more effectively to infections encountered more than once.
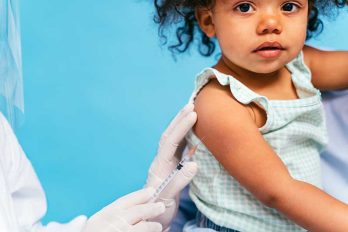
The Impact of Vaccinations
Vaccines are important during infancy because they help educate the adaptive immune system. Vaccines mimic infections, allowing the infant’s immune system to generate memory cells against certain pathogens without the child contracting the diseases caused by these pathogens. This is especially critical in the infant’s first few months, when the immune system is still learning how to defend itself efficiently.
Challenges and Immune Responses
Infants may be more susceptible to infections throughout the first year of life as their immune systems grow and adapt. This is a natural part of the process. Common mild illnesses help the immune system develop a more thorough defense. However, at this time, keep an eye out for evidence of unusual immune responses or more severe infections, which can suggest issues with immune system development.
Supporting Immune Development
Parents and caregivers can help an infant’s immune system grow by providing sufficient nourishment, keeping the surroundings clean and safe, and adhering to prescribed vaccination regimens. Additionally, enabling natural exposure to ordinary infections, such as those prevalent in a regular household, can aid in the development of a healthy immunity.
The first year of an infant’s life is essential for immune system development. It lays the groundwork for a strong immune response that will safeguard the child throughout life. Understanding and supporting its development through proper nutrition, vaccination, and exposure to the environment can help infants establish a strong immune system. This journey, despite its intricacy, is critical in preparing children to face the difficulties of the world around them.